Contractors are increasingly choosing Type MC cable (metal-clad) as an alternative to traditional pipe and wire electrical system installations.
Article 330 of the National Electrical Code (NEC) gives three key features of metal-clad armored cables:
- Conductors are inside a metal sheath or tape
- Conductors are insulated
- Cable is factory assembled
Generally, you should secure MC cable every six feet and within 12 inches of a termination. You should secure the cable every three feet if it is attached to equipment or in a place where it will experience vibration.
With options such as strut support systems, straps and clamps, and cable trays, there are many ways to make MC cable look as good as conduit with less effort.
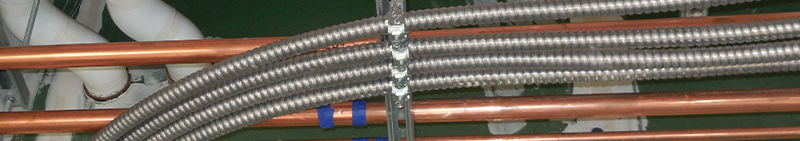
There are a few situations where you should adjust the ampacity of each conductor according to Table 310.15(C)(1) of the NEC to avoid overheating:
- If you are installing MC cables in contact with insulation, caulk, or sealing foam

- If there are three or more cables touching each other

- If the cables contain two or more current-carrying conductors per cable

Some projects require an MC cable to be exposed to harsh elements, or to be buried. In these cases, a jacketed cable, such as Service Wire's Jacketed MC—rated for wet conditions, exposure, and direct burial—should be used. When installing in wet areas, you must use liquid tight connectors to ensure no moisture gets to the cable or termination.
MC CABLE IN HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS
You can use Service Wire MC cable in hazardous locations, including Class I-Division 2 and Class II-Division 2 zones. Class refers to the type of flammable substance, and Division (or Div) refers to the type of area where work is happening.

- Div 2 areas are those where flammable substances are unlikely to exist during normal operating conditions.
- Class I substances are flammable gas, vapors, and liquids.
- Class II substances are combustible dusts.